- Joined
- Jul 25, 2005
- Messages
- 3,237
Penis
covered by sup/deep fascia of penis

General Info:
1. Root
inf ramus of pubis (crus) –> midline of UG diaphragm (bulb) –> penile urethra
located in superficial perineal pouch, b/w perineal membrane sup, and deep perineal fascia inf
Crus of penis = covered by ischiocavernosus m
Bulb of penis = covered by bulbospongiosus m
* More info on these musc/structures will be covered in male perineum
2. Body (shaft)
3 cavernosus bodies:
2 corpus cavernosa
1 corpus spongiosum
has very little muscular fibers in this part
has thin skin, CT, blood & lymph vessles, fascia and the corpora
fill w/ blood during sexual excitement –> erection
Each cavernous body has strong fibrous CT capsule = tunic albuginea

Corpus cavernosum:

Lymph Drainage: superficial lymph nodes
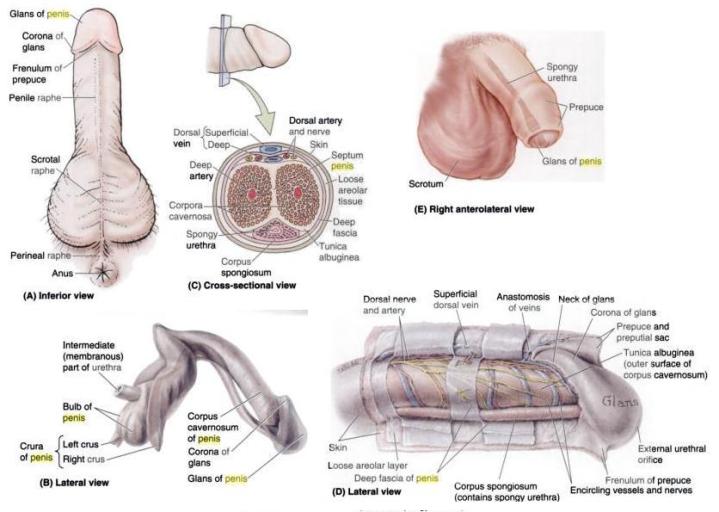
covered by sup/deep fascia of penis
- b/w the 2 fascia = dorsal cutaneous v
- below = dorsal v in midline, L & R dorsal a lat to it, and most lat is dorsal n

General Info:
- held in back to perineal body (w/ bulbospongiosus m)
- goes through perineal membrane
- lat = fibromuscular tissue = triangular shape
- Function: sexual intercourse, urination
- Fundiform lig – from linea alba & membranous layer of sup fascia of abdomen –> splits into L& R parts –> encircles body of penis –> blends w/ superficial penile fascia –> scrotum septum
- Suspensory lig of penis – pubis symphysis and arcuate pubic lig –> deep fascia of penis or body of clitoris
- lies deep to fundiform lig
- Deep fascia of penis (Buck’s fascia) – continuation of deep perineal fascia, cont w/ fascia covering ext oblique m & rectus sheath
- Tunica albuginea – dense fibrous layer that envelopes both corpora cavernosa & corpus spongiosum
- very dense around corpus cavernosa –> impede venous return & result in extreme rigidity of structures when erectile tissue become engorged w. blood
- more elastic around spongiosum, therefore not turgid during erection, permist passage of ejaculate
- Tunica vaginalis – double serous membrane, peritoneal sac @ end of process vaginalis
- covers front and sides of testis and epididymis
- closed sac derived from ab peritoneum, forming innermost layer of scrotum
- parietal layer = adjacent to int spermatic fascia
- visceral layer = adherent to testis & epididymis
1. Root
inf ramus of pubis (crus) –> midline of UG diaphragm (bulb) –> penile urethra
located in superficial perineal pouch, b/w perineal membrane sup, and deep perineal fascia inf
Crus of penis = covered by ischiocavernosus m
Bulb of penis = covered by bulbospongiosus m
* More info on these musc/structures will be covered in male perineum
2. Body (shaft)
3 cavernosus bodies:
2 corpus cavernosa
1 corpus spongiosum
has very little muscular fibers in this part
has thin skin, CT, blood & lymph vessles, fascia and the corpora
fill w/ blood during sexual excitement –> erection
Each cavernous body has strong fibrous CT capsule = tunic albuginea

Corpus cavernosum:
- long rod like structures
- from bulk of penis body
- fibromuscular tissue
- Crus of penis lead to corpus cavernosum
- fuse @ midline
- contains the deep a of penis
- tunica albuginea of corpus cavernosa fuse @ midling = form septum penis
- b/w & below carvernosa
- tunica albuginea thinner & weaker & blends w. tunic of cavernosum
- carries the urethra
- bulb leads to corpus spongiosum
- NEVER hardens! (otherwise, would depress urethra, no ejaculation)
- is the head of the penis
- continous w/ foreskin @ coronal sulcus, and via frenulum
- sep from body via corona glandis (sulcus) and location of glands that release the pre-ejaculate
- exit of urethra is on ant tip of glans = vert slit
- extention of corpus spongiosum, and is therefore also soft in erection
- covered by foreskin
- br of int pudendal a
- dorsal a – run in space b/w corpora cavernosa, lat to deep dorsal v
- deep a – peirce crura, run w/in corpora cavernosa
- supply cavernosus spaces in erectile tissue of corpora cavernosa
- gives branches called the helicine a
- a of bulb of penis – supply post corpus spongiosum, bulbourethral gland
- ext pudendal a - supply penile skin
- vein drainage
- dorsal v of penis in deep fascia –> prostatic venous plexus
- superficially, –> superficial dorsal v –> superficial ext pudendal v or lat pudendal v

Lymph Drainage: superficial lymph nodes
Erection:
also involves contraction of bladder sphincter –> so no urine –> urethra and no semen goes into bladder
Bulbospongiosus m –> propelling force of ejaculation
- Deep a of penis –> br into helicine a, that run radially & open into cavernae
- Veins (which drain cavernae) are located in periphery of corpus cavernosum, beside tunica albuginea
- Helicine a have special smooth m valves = Ebner’s cushions, usually closed & allows minute amount blood in, drained easily by veins
- During sexual excitement, Ebner’s cushions open & blood suddenly flow in and fill up cavernae
- Blood influx compresses veins, so no blood is drained = ERECTION
- @ end of erection, Ebner’s cushions close, blood flow dec & vein compression release –> cavernae empty
also involves contraction of bladder sphincter –> so no urine –> urethra and no semen goes into bladder
Bulbospongiosus m –> propelling force of ejaculation





























